Primary Solution Areas

Specialty Laboratory and Biomarker Services
Cerba Research has an extensive history providing specialty lab and biomarker services. It’s in our DNA. Benefit from our customized service to obtain innovative, flexible solutions grounded in scientific expertise.

Clinical Trial Services
Leverage our global logistical and laboratory network, covering five continents. Cerba Research’s agile, customer-centric approach helps support the management of your clinical trials.
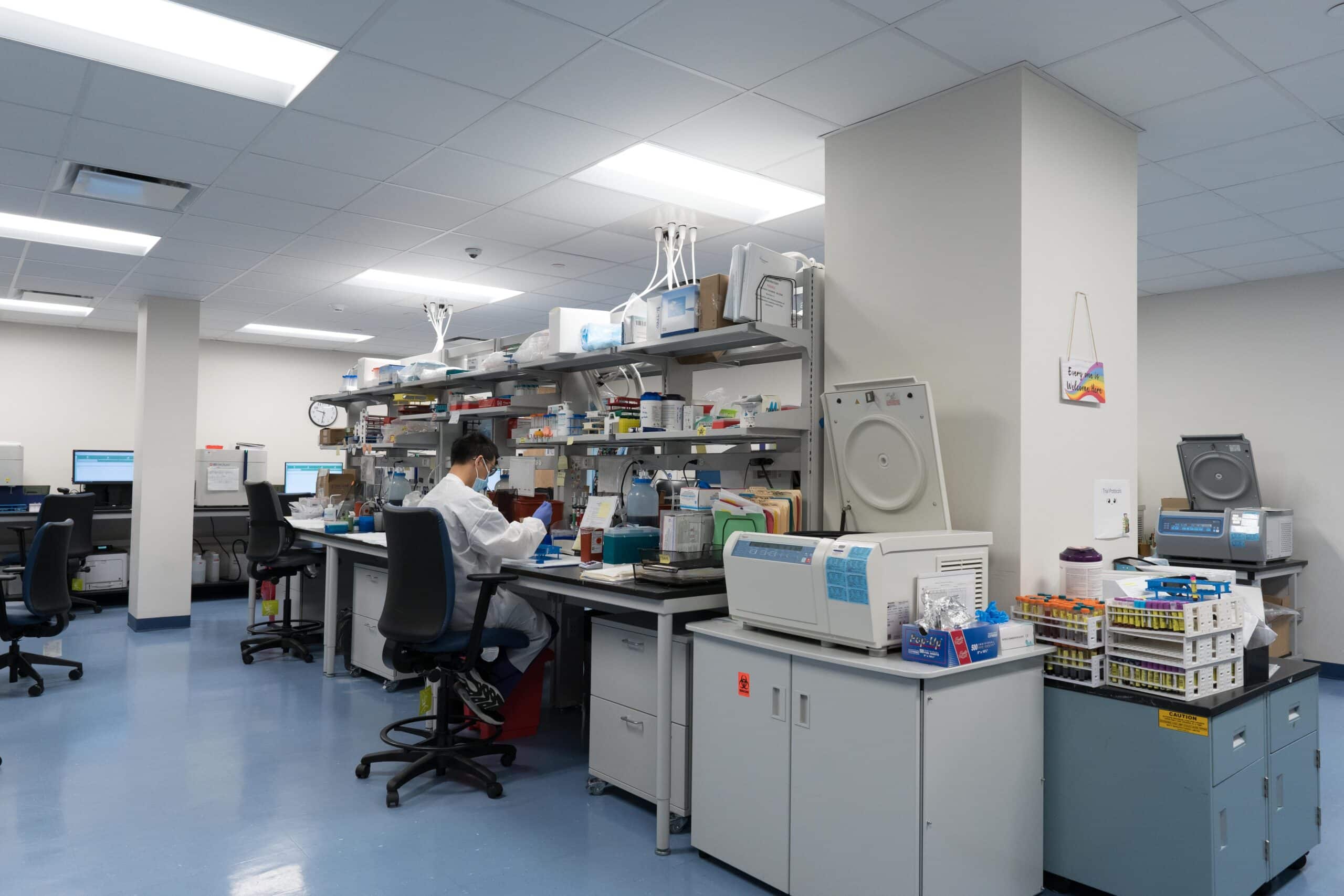

Therapeutic Areas & Scientific Expertise
With our unparalleled scientific expertise, the fast-expanding portfolio of therapeutic areas include oncology, metabolic diseases, virology, infectious Inflammatory, autoimmune and rare diseases.
Infectious Disease & Vaccine Development
We provide world-class operational expertise, logistical infrastructure, and the scientific rigour needed to effectively characterize, research, and treat infectious diseases as they emerge.
We deploy an expert global team who can utilise their experience, their knowledge and the best technologies available to accelerate clinical trials and ultimately reduce the burden of infectious disease. We do this empowered by our people, science, and technology and infrastructure.

Rare Diseases
We facilitate state-of-the art technology, subject matter expertise, specialised logistics and operations to accelerate cell and gene therapy development.
Additionally, we ensure global distribution of sample kits, providing easy access worldwide. Our specialized pick-up and transport services maintain the integrity of samples by utilizing dry ice and ensuring global coverage.

Oncology
Immuno-oncology and personalized medicine have sparked a new era in cancer research but working with a global patient base can be challenging.
Cerba Research can shape and advance your complex trial by leveraging industry-leading labs, patient databases, and our network of scientific experts spanning five continents.
Together, we can accelerate your program to market.


Our mission
To shape and advance clinical trial research by leveraging patient data and scientific insight. This is achieved by providing customized laboratory solutions that support global biotech, pharma, IVD, and research organizations, improving the lives of patients around the world.
Sector Expertise

Pharmaceutical
We have an extensive history of supporting businesses in the pharmaceutical industry, constantly evolving to meet ever-changing demands.

Biotech
Cerba Research is the precision medicine partner of choice for a number of companies operating in the biotechnology industry. Our capabilities are always adapting and evolving to match increasingly complex needs.

CRO
We collaborate with Contract Research Organizations to drive clinical research forward and develop tailored solutions to unique industry challenges.

Non-profit
When working with Cerba Research as a non-profit organization, our expertise becomes your expertise. We can lend the support you need to drive research forward.
Government
Familiar working with Government agencies on projects including Operation Warp Speed, Government Task Forces in response to the Pandemic as well as Health Agencies, we bring the best of both worlds of speciality and central laboratory expertise to be able to scale up to face global health demands.
IVD/Medical Device
Cerba Research partners with IVD/MDDx research bodies to shape future research. We have the knowledge and expertise to guide you through approaching regulatory changes and help keep you at the forefront of accurate diagnostics.
Recent News

Viroclinics-DDL changes name to Cerba Research

Why a multi-faceted oncology toolkit is essential for precision medicine

Cerba Research Global Project Management Communication On Public And National Holidays 2024

Get in touch with us today to find out how we can support your clinical research ambitions.
Contact Us